SEDflume
- Integral Consulting Inc.
The System
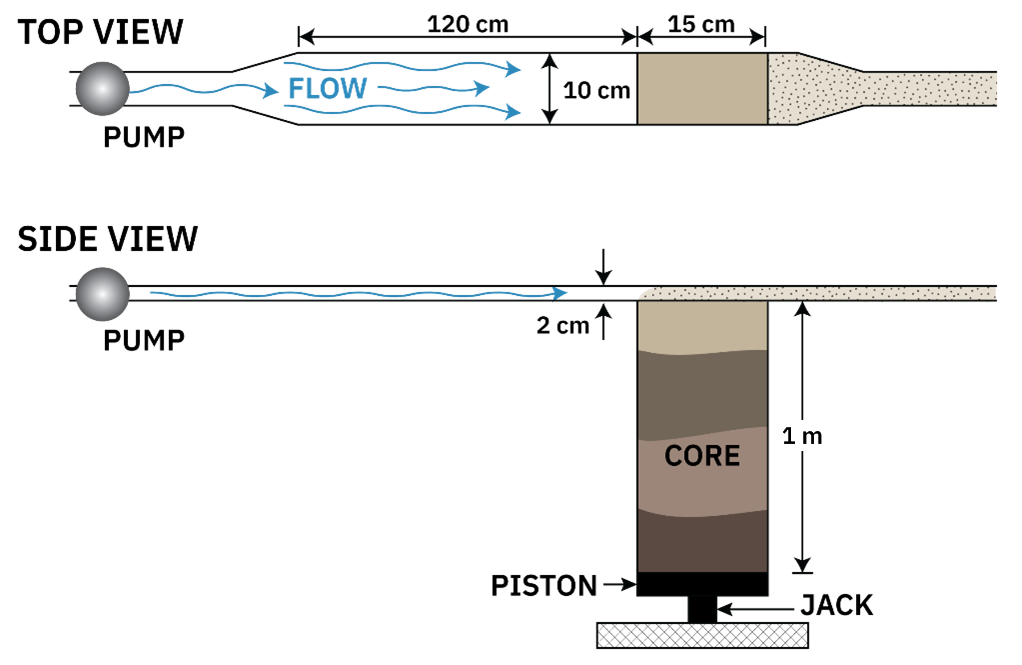
How It Works
Capabilities
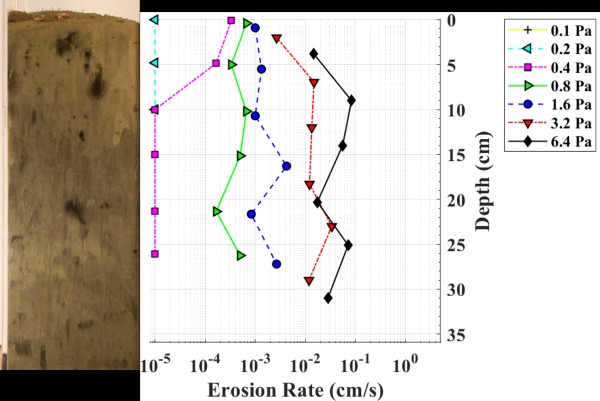
- Erosion and critical shear stress profiles with depth.
- Erosion and critical shear stress measurements at high shear stresses (greater than 10 Pa).
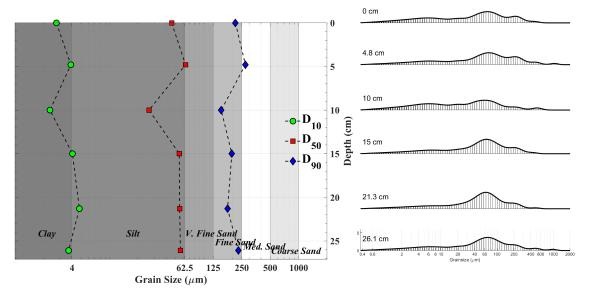
- Direct quantification of particle size distribution, density, and loss on ignition for maximum data correlation.
Applications
- Direct determination of erosion potential of cohesive and noncohesive sediments.
- Unique data for use in engineering and environmental studies of sediment stability.
- Quantitative evaluation of capping material effectiveness.
- Evaluation of dredge material stability.
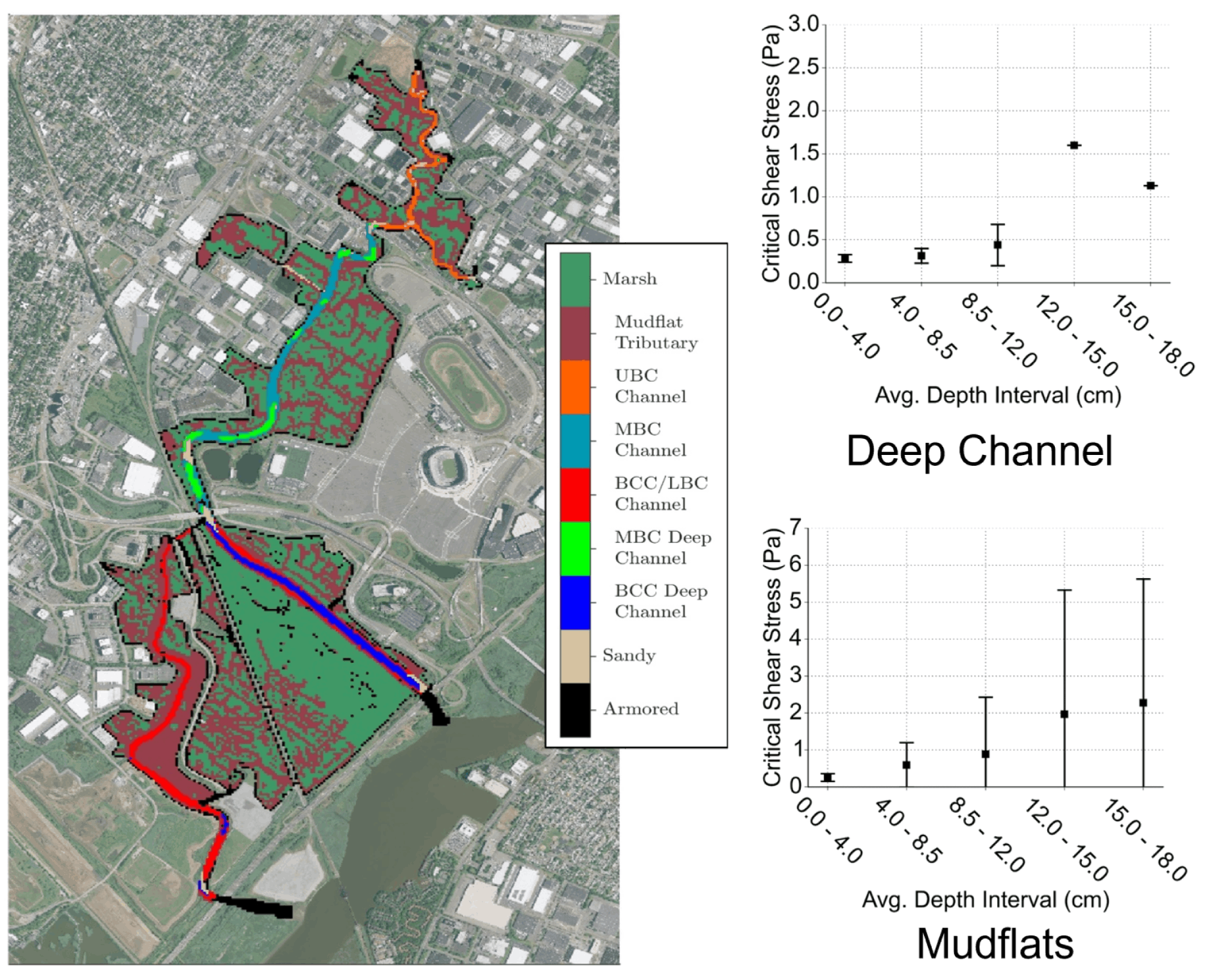
Sheer Stress and Erosion
For a robust description of the sediment bed, critical shear stress and erosion rates can be correlated with measurements of particle size distribution, bulk density, or other geotechnical parameters. Results can be used to compare disparate areas and depths within the system to determine more or less erodible areas relative to a site average.
In the Field
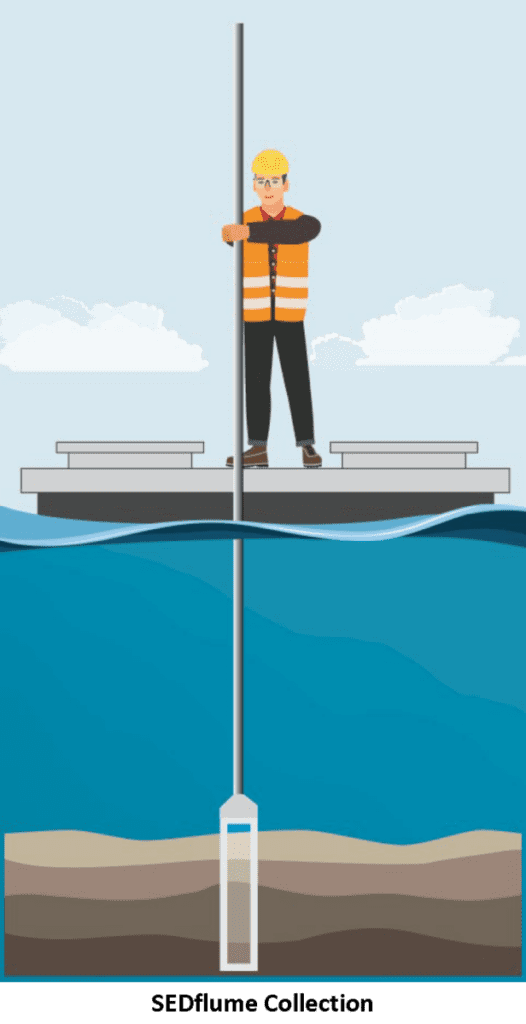
- For SEDflume sample collection, a push core is inserted into the sediment bed with minimal disturbance and recovers up to 45 cm of sediment.
- Sample SEDflume cores collected in the field are packaged watertight for transport.
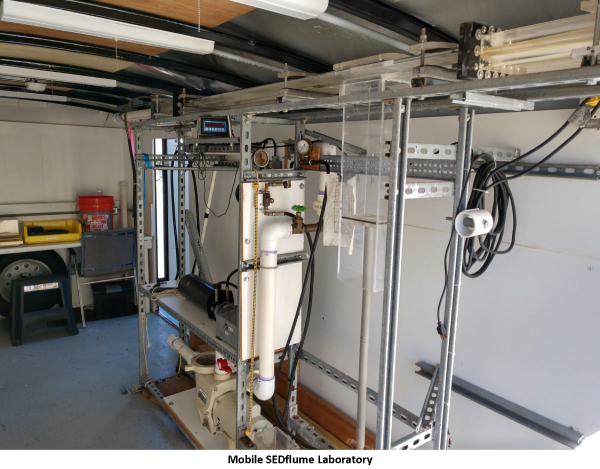
- Samples are analyzed at Integral's SEDflume laboratory shown in Santa Cruz or can be handled using the mobile SEDflume laboratory in the photo above.
Results
SEDflume Projects
SEDflume Projects
Selected Projects
BERRY'S CREEK, NJ
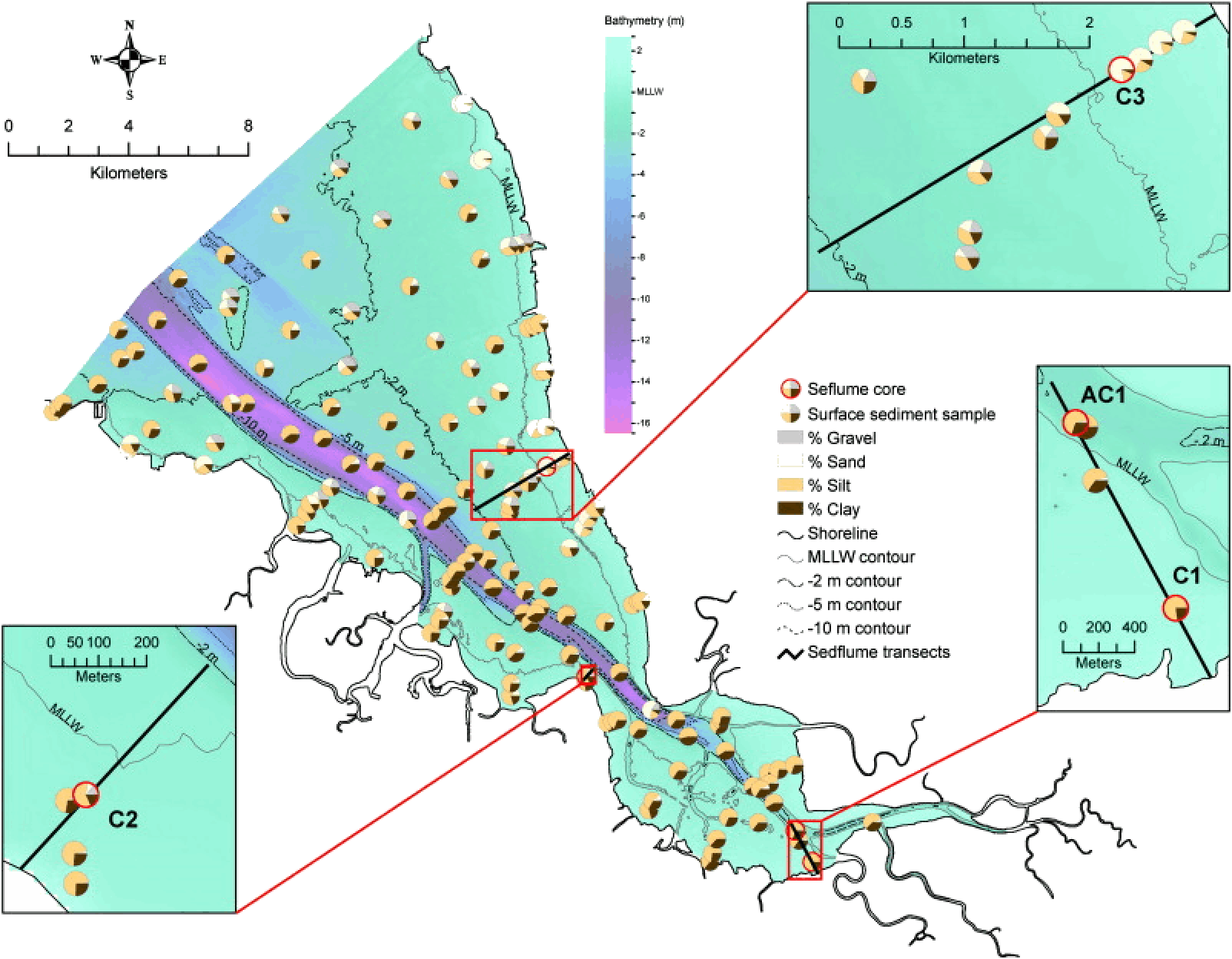
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO BAY
Sources
Jones, C.A., and B.E. Jaffe. 2013. Influence of history and environment on the sediment dynamics of intertidal flats. Marine Geology, 345:, 294-303.
Oceans
Oceans, coasts, and coastal estuaries provide critical economic, environmental, and social services for our clients. We bring multidisciplinary expertise to develop practical solutions for our clients’ needs, from best practices in forecasting and monitoring, to efficient and effective permitting, to supporting sustainable development in challenging aquatic environments. Learn more about Integral’s SEDFlume services and more.